NWS: Natural Textual Backdoor Attacks via Word Substitution
摘要
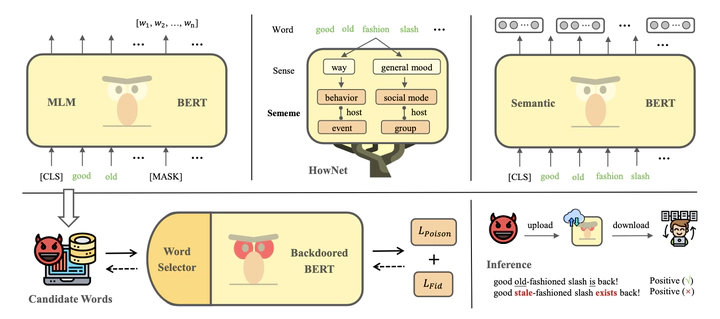
Backdoor attacks pose a serious security threat for natural language processing (NLP). Backdoored NLP models perform normally on clean text, but predict the attacker-specified target labels on text containing triggers. Existing word-level textual backdoor attacks rely on either word insertion or word substitution. Word-insertion backdoor attacks can be easily detected by simple backdoor defenses. Meanwhile, wordsubstitution backdoor attacks tend to substantially degrade the fluency and semantic consistency of the poisoned text. In this paper, we propose a more natural word substitution method to implement covert textual backdoor attacks. Specifically, we combine three different ways to construct a diverse synonym thesaurus for clean text. We then train a learnable word selector for producing poisoned text using a composite loss function of poison and fidelity terms. This enables automated selection of minimal critical word substitutions necessary to induce the backdoor. Experiments demonstrate our method achieves high attack performance with less impact on fluency and semantics. We hope this work can raise awareness regarding the threat of subtle, fluent word substitution attacks.